说明
本应用说明介绍了如何将电解式倾斜传感器的原始输出转换成度数。
倾斜传感器的线性范围和工作范围
An electrolytic tilt sensor’s measurement range can be described in two ways: linear range and operating range. The operating range is the range over which the sensor will give a monotonic output but otherwise has no defined characteristics (it is non-linear). The linear range is the portion of the operating range where the output is linear to within a certain percentage. Figure 1 shows the difference between the two ranges.
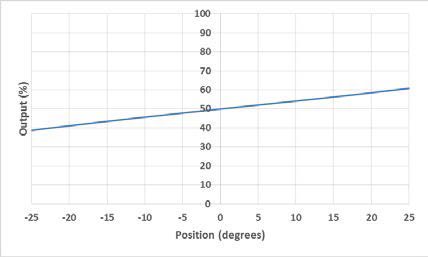
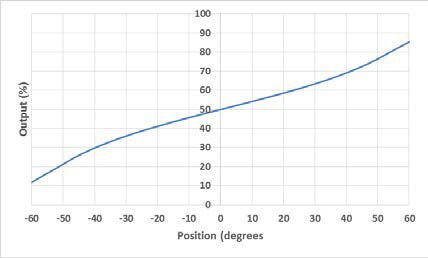
图1线性范围(左)和工作范围(右)。
线性近似
To find the tilt angle within the linear range, it is necessary to find a linear function that matches the output of the sensor. This will be the function of the line in the left graph in Figure 1. This function is given below:
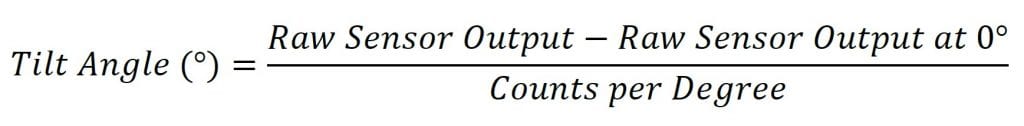
本公式中的原始传感器输出是传感器的输出。这通常是以计数为单位,但根据传感器输出的读取方式,也可以使用其他单位。
其他两个值需要以一定的角度对传感器进行取样。这些角度可以使用另一个传感器、数字量角器或任何其他确定角度的方法来确定。0°时的原始传感器输出只是传感器处于水平状态时的输出。
The counts per degree (which is the slope of the line) are calculated using the following formula:
![]()
The linear range is obtained from the datasheet for the sensor. The raw outputs will be the sensor output at the edges of the linear range. For example, for a sensor with a linear range of ±25°, the raw outputs would be sampled at +25° and -25°. Note that these samples will only need to be taken once to create the function; converting tilt can then be done using the sampled values.
Let’s say we have a 0717-4319-99 sensor with a 16-bit (0 to 65535) output we would like to convert to degrees. This is a dual axis sensor with a linear range of ±20°. Since it is a dual axis sensor, we will need 2 formulas: one for the X axis and one for the Y axis. First, we will find the X axis formula. We start be taking samples at 0° and ±20° and find the following measurements.
X轴在-20°时的倾斜度=26055。
X轴在0°时的倾斜度=33234。
X轴倾斜度为±20°=40379。
现在我们可以用这些样本来计算每度的计数。
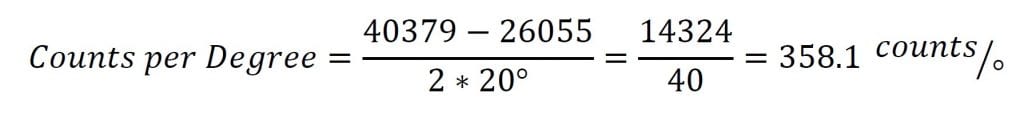
The counts per degree and zero samples can then be plugged into the formula to give the conversion below:

如果需要进行Y轴测量,请按照这些步骤从Y轴的样品再次进行测量。
Now, whenever we have a measurement from this sensor we would like to convert to degrees, we can use this new formula.
For example, if we have an X output of 29655, we can use the formula to determine the tilt angle:
![]()
每个学位的大约数量
由于制造工艺造成的细微差异,应计算每个特定传感器的转换函数。然而,这并不总是可行的。下表给出了可用于计算的每度平均计数和0°值。请注意,与为特定传感器创建函数相比,使用这些值将导致较低的测量精度。所有数值均为16位(0-65535)输出。表中未列出的传感器将要求用户按照上述程序查找转换。
| 传感器 | 每度数 | 零度 |
| ApexTwo™ | 284 | 32768 |
| F203-00A-212-00 | 17582 | 32768 |
| F225-00T-003-01 | 976 | 32768 |
| 0703-0711-99 | 17582 | 32768 |
| 0703-1602-99 | 976 | 32768 |
| 0703-1603-99 | 976 | 32768 |
| 0717-4303-99 | 736 | 32768 |
| 0717-4304-99 | 268 | 32768 |
| 0717-4305-99 | 188 | 32768 |
| 0717-4306-99 | 188 | 32768 |
| 0717-4311-99 | 268 | 32768 |
| 0717-4313-99 | 342 | 32768 |
| 0717-4314-99 | 335 | 32768 |
| 0717-4316-99 | 756 | 32768 |
| 0717-4317-99 | 569 | 32768 |
| 0717-4318-99 | 284 | 32768 |
| 0717-4319-99 | 363 | 32768 |
| 0717-4321-99 | 758 | 32768 |
| 0717-4322-99 | 594 | 32768 |
| 0729-1751-99 | 284 | 32768 |
| 0729-1752-99 | 284 | 32768 |
| 0729-1753-99 | 284 | 32768 |
| 0729-1754-99 | 284 | 32768 |
| 0729-1755-99 | 284 | 32768 |
| 0729-1759-99 | 284 | 32768 |
| 0729-1760-99 | 284 | 32768 |
| 0729-1765-99 | 976 | 32768 |
| 0729-1767-99 | 284 | 32768 |
| 0729-1768-99 | 284 | 32768 |
| 0729-1769-99 | 284 | 32768 |
| 0737-0101-99 | 2887 | 32768 |
| 0737-1203-99 | 41942-57670 | 32768 |
多点插值
多点插值法使用提前采集的样本来得出度数的测量结果。这种方法的精度将取决于样本的数量和分布;然而,即使是取3个样本,一般也能提供比线性近似更好的结果。
Sample distribution is one of the most important factors in reaching an accurate conversion. Conversions close to samples will be more accurate. Because of this, samples taken closer together will result in more accurate conversions. These samples should be taken across the entire range of the sensor. Depending on the application, they can be evenly dispersed evenly across the entire range or focused in one region where precision is necessary.
To convert a raw value to degrees, identify two reference samples. These are the two samples that are closest to the measurement in each direction. Then, find a linear approximation between the two samples and map the raw output onto this approximation. The point on this line will give the sensor’s tilt in degrees. The graph in Figure 2 shows a visualization of this concept.
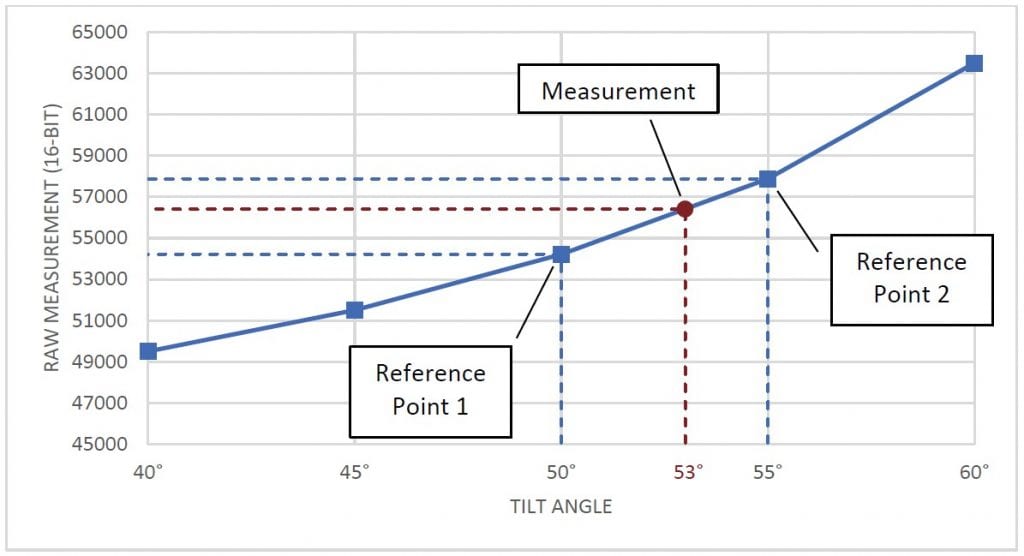
图2显示样品、参考样品和测量的图表。
这个换算公式如下所示。
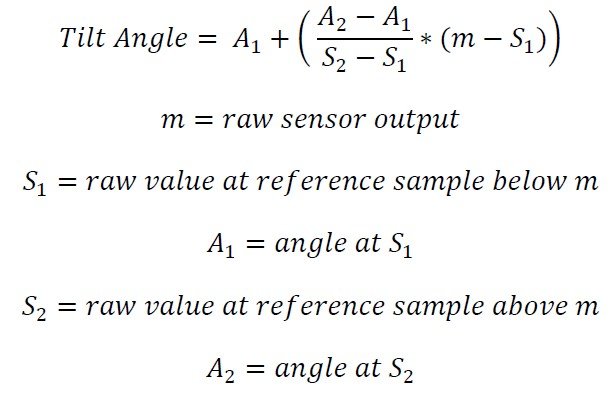
假设我们有一个工作范围为±60°的倾斜传感器的56412的原始测量值。另外,假设我们已经以5°的间隔采集了样本用于转换。通过比较56412和样本,我们确定我们的两个参考点将在50°(54213)和55°(57878)。然后,我们可以使用公式来计算角度。
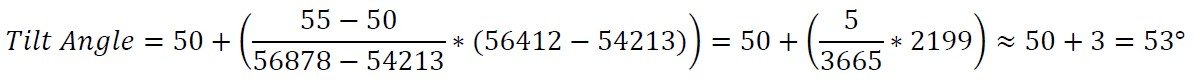
因此,我们最终的测量结果是53°。
此方法可用于将传感器工作范围内任何地方的测量值转换为度数。它也将实现比线性近似更好的精度。然而,它需要大量准确的样本才能达到最佳效果。
多项式插值
多项式插值可用于实现精确的测量,而无需采集许多样本。这种方法将使用样本找到一个多项式方程,该方程将在传感器的工作范围内提供准确的转换。
The samples taken will be used to develop a polynomial equation that will describe the sensor output. At a minimum, you will need N-1 samples to derive a degree N polynomial. For example, 7 samples will create a degree 6 polynomial. You can also use more samples to create a lower degree polynomial, but this will generally have lower accuracy than creating a
higher degree polynomial with the same points.
可以使用任何数量的样本,但我们建议至少取3个样本。使用2个样本也可以,但会导致线性近似。需要注意的是,7级或更高的多项式对精度的提高不大。
While the polynomial can be determined manually, it is much easier to calculate it using software. One simple method is to use Microsoft Excel’s line of best fit; however, this will may not be precise enough for a usable conversion. Wolfram Alpha is a more accurate option, but the equation will still have to be solved manually. The best option is to use a programming library. For example, the Polynomial.fit() method from the NumPy Python library can be used. The code below shows how this can generate a 6th order polynomial from 7 points:
导入numpy.polynomial.polynomial。 coefficients = numpy.polynomial.polynomial.Polynomial.fit( [56668, 46553, 36140, 32845, 31207, 21913, 9586], # 原始值 [60,42,12,0,-6,-36,-60],#对应的角度值为原始值。 6)#多项式的阶数 print(coefficients) # 产出。 # [-7.88427627e+01 2.57631617e-03 # [-7.88427627e+01 2.57631617e-03 -7.71958174e-08 -1.75354175e-13 # 2.17551410e-16 -5.89635260e-21 4.45379575e-26]
请注意,当使用这样的函数时,正确指定顺序是很重要的。例如,4个样本将生成一个3阶多项式。然而,如果给定4作为顺序,库将随机猜测来创建一个方程。这将导致不那么精确的转换。
The array returned by Polynomial.fit() are the coefficients of the polynomial. Based on the output above, the equation
would be:
角度= (4.45e-26)x6- (5.89e-21)x5+ (2.17e-16)x4- (1.75e-13)x3- (7.72e-8)x2+ (2.57e-3)x1- 78.84。
这个函数就可以通过插入x的原始值来解决未知角度,比如说我们有上面的函数,有一个41643的原始测量值。我们可以用下面的计算方法来求角。
角度= (4.45e-26)(41643)6- (5.89e-21)(41643)5+ (2.17e-16)(41643)4- (1.75e-13)(41643)3- (7.72e-8)(41643)2+ (2.57e-3)(41643)1- 78.84
角度= 232.264 - 738.402 + 654.227 - 12.663 - 133.868 + 107.285 - 78.842 = 30.002°。
If using the NumPy library shown above, this can be done using the polyval() method.
print(numpy.polynomial.polyval(41643, coefficients.convert(.coef)) # 输出:30.001695321007
Note that the result of this calculation is very sensitive to any change in input. For example, if the coefficients above are rounded to 3 significant digits (as written), the result of the equation is 31°. Because of this, it is important not to round any values while calculating the angle with this method.





